Six policies to reduce economic inequality

Following the Inequality Policy Brief, here are six ways to minimize the rising economic inequality prevalent in the United States. Haas Institute Director john a. powell discusses why these policies will work in slowing the growth in inequality.
Toward this goal, researchers from the Haas Institute for a Fair and Inclusive Society at UC Berkeley point to the following six evidence-based policy solutions that can have a positive effect on reversing rising inequality, closing economic disparities among subgroups and enhancing economic mobility for all:
1. Increase the minimum wage.
Research shows that higher wages for the lowest-paid workers has the potential to help nearly 4.6 million people out of poverty and add approximately $2 billion to the nation's overall real income. Additionally, increasing the minimum wage does not hurt employment nor does it retard economic growth.
2. Expand the Earned Income Tax.
In recent years, the EITC has been shown to have a positive impact on families, lifting roughly 4.7 million children above the poverty line on an annual basis. Increases in the EITC can pull more children out of poverty while providing more economic support for the working poor, especially single parents entering the workforce.
Policies that encourage higher savings rates and lower the cost of building assets for working and middle class households can provide better economic security for struggling families. New programs that automatically enroll workers in retirement plans and provide a savings credit or a federal match for retirement savings accounts could help lower-income households build wealth.
4. Invest in education.
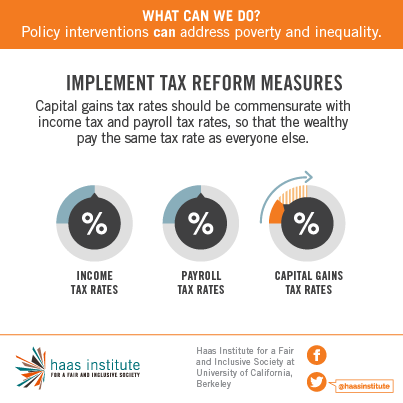
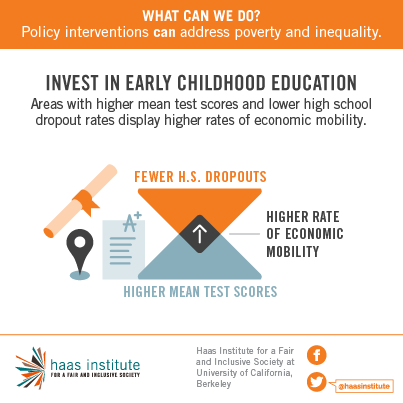
Differences in early education and school quality are the most important components contributing to persistent inequality across generations. Investments in education, beginning in early childhood with programs like Head Start and Universal Pre-K, can increase economic mobility, contribute to increased productivity and decrease inequality.It is a great irony that tax rates for those at the top have been declining even as their share of income and wealth has increased dramatically. The data show we have created bad tax policy by giving capital gains -- profits from the sale of property or investments -- special privileges in our country's tax code; privileges that give investment income more value than actual work. Capital gains tax rates must be adjusted so that they are in line with income tax rates. Savings incentives structured as refundable tax credits, which treat every dollar saved equally, can provide equal benefits for lower-income families.
Higher levels of racial residential segregation within a metropolitan region are strongly correlated with significantly reduced levels of intergenerational upward mobility for all residents of that area. Segregation by income, particularly the isolation of low-income households, also correlates with significantly reduced levels of upward mobility. Eliminating residential segregation by income and race can boost economic mobility for all.
Each of these policies, if carefully implemented, has the potential to lift working families out of poverty, support greater economic mobility and/or reduce the growth of inequality. All of these policies could be enacted at the local, state and federal levels if there is political will. While there is still some disagreements of the best way to reduce inequality, there is a growing consensus that inequality should be reduce.
Recently the IMF joined this consensus in finding that inequality reduces overall economy growth as well as challenges basic democratic principle and fairness. But getting policymakers to prioritize these policies will depend on the actions of advocates, voters and other supporters with a vision for a fair and inclusive society so strong that they overwhelm powerful forces that seek to maintain the status.





Comments
Post a Comment